A new report on Tuesday showed the growth of electronic espionage stations in Cuba linked to China, including new construction about 70 miles from the US naval base in Guantanamo Bay.
This study by the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), a group of experts based in Washington, followed up on a report from The Wall Street Journal last year that pointed to negotiations between China and Cuba to strengthen ties in defense and intelligence, including a new joint military and espionage training facility on the island.
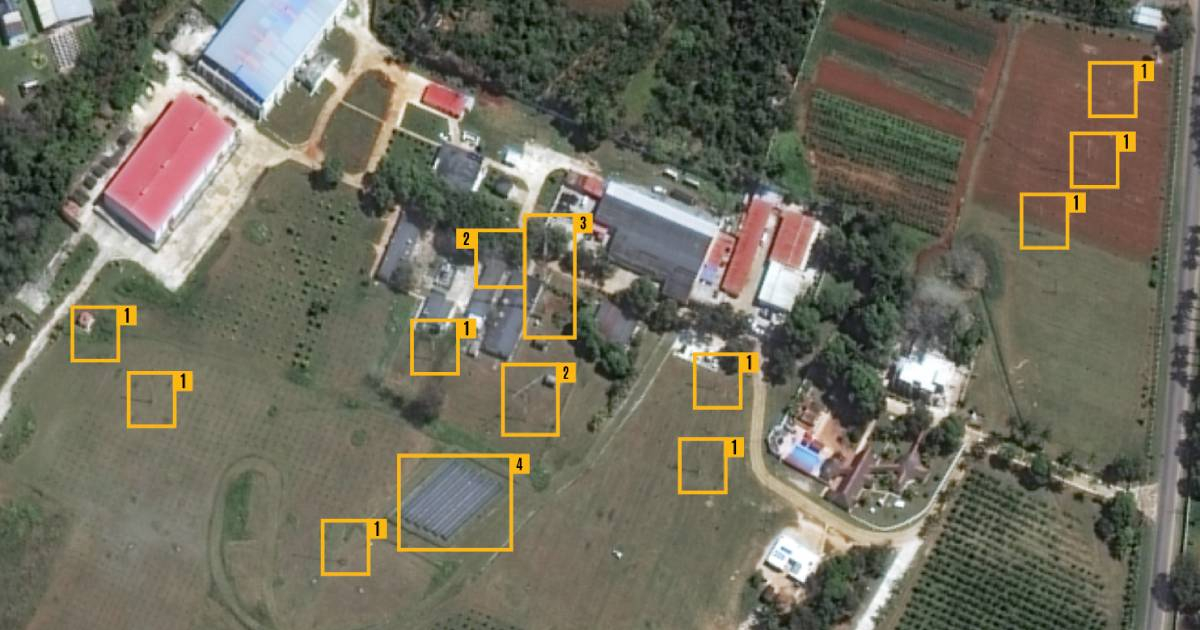
Satellite images and information from open sources evaluated by the CSIS offer an unprecedented view of four active sites in Cuba capable of conducting electronic surveillance operations.
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is a central element of modern espionage, and intercepting signals transmitted by both civilian and military actors can provide countries with valuable information about their adversaries, competitors, and allies alike.
The study center explains that collecting SIGINT is a complex task that requires specialized equipment, that is, antennas optimized for the signal characteristics of their targets; as the size, number, orientation, and arrangement of these antennas determine their capabilities and functions.
It says that for SIGINT, parabolic antennas are also used, which can focus radio waves into a narrow beam, making them effective for communicating with satellites far from Earth, as well as for intercepting and collecting signals from various sources. Radar antennas emit and receive radio waves to track physical objects such as ships, airplanes, and missiles, it details.
Although the Cuban regime denied the existence of Chinese espionage bases, this study shows the ambitions of the Asian nation to expand its global intelligence collection capabilities, which have led them to establish a presence close to the United States.
In 2023, officials from the Joe Biden administration revealed that China has access to multiple espionage facilities in Cuba. Although Chinese activities on the island remain secret, satellite images analyzed by the CSIS provide the most comprehensive assessment of the likely locations where China is operating.
Locations of the spy bases in Cuba according to the CSIS study
Bejucal: Located in the hills near Havana, this Cuban SIGINT facility is the largest reviewed by CSIS. Known for housing Soviet nuclear weapons during the Missile Crisis in 1962, Bejucal has been suspected of having links to Chinese intelligence. Satellite images from March 2024 show significant upgrades, including the construction of a new radome that could contain a radar or ELINT system.
2. El Salao: Located in the eastern part of Santiago de Cuba, this new SIGINT complex had not been previously reported. Initiated in 2021, the site appears to be a large CDAA with a diameter ranging from 130 to 200 meters, capable of enhancing aerial and maritime surveillance in the region.
3. Wajay: Located less than 10 kilometers north of Bejucal, this smaller facility has 12 antennas of various sizes and orientations, and it is believed to be used for intercepting and transmitting terrestrial signals. Unconfirmed rumors suggest that China played a role in its construction or modernization.
4. Calabazar: This small military complex near Calabazar, documented in declassified files from the U.S. government, shows typical characteristics of SIGINT operations, with more than a dozen parabolic and pole antennas. Its evolution suggests continuous adjustment to the assigned missions.
The current report also mentions the historic Lourdes Signals Intelligence Complex, operated by the Soviet Union during the Cold War, as another emblematic espionage site in Cuba.
Cuba's proximity to the southern United States and the Caribbean makes it a privileged location for the collection of SIGINT, allowing China significant intelligence access not available from its own territory.
Surveillance of military activities and communications in the region could provide valuable data to China about American military practices, even when modern communications are highly encrypted.
What do you think?
COMMENTFiled under: