Though Cuba is not situated in one of the most seismically active areas in the world, it has experienced significant earthquakes that have left a deep mark on its history and in the memory of its people.
These events have primarily occurred in the eastern region of the island, due to the influence of the Oriente fault, one of the main seismic zones in the Caribbean.
Major earthquakes in the history of Cuba
The record of significant earthquakes in Cuba begins in 1528, with a VI intensity tremor in Baracoa, about which no additional information is available.
Since then, numerous significant events have been documented, primarily in the eastern region of the island.
One of the oldest and deadliest earthquakes occurred on June 11, 1766, in Santiago de Cuba, with an estimated magnitude of 7.6. This earthquake destroyed a large part of the city, including churches and government buildings, resulting in 120 fatalities and over 600 injuries.
It had many aftershocks, primarily in the 48 hours that followed. It was noticeably felt in Havana and in the neighboring island of Jamaica.
Another important event took place on August 20, 1852, also in Santiago de Cuba.
With an estimated magnitude of 7.2, this earthquake caused panic and resulted in two deaths, a dozen injuries, and structural damage to over 600 buildings, including the Metropolitan Cathedral, which had to be rebuilt.
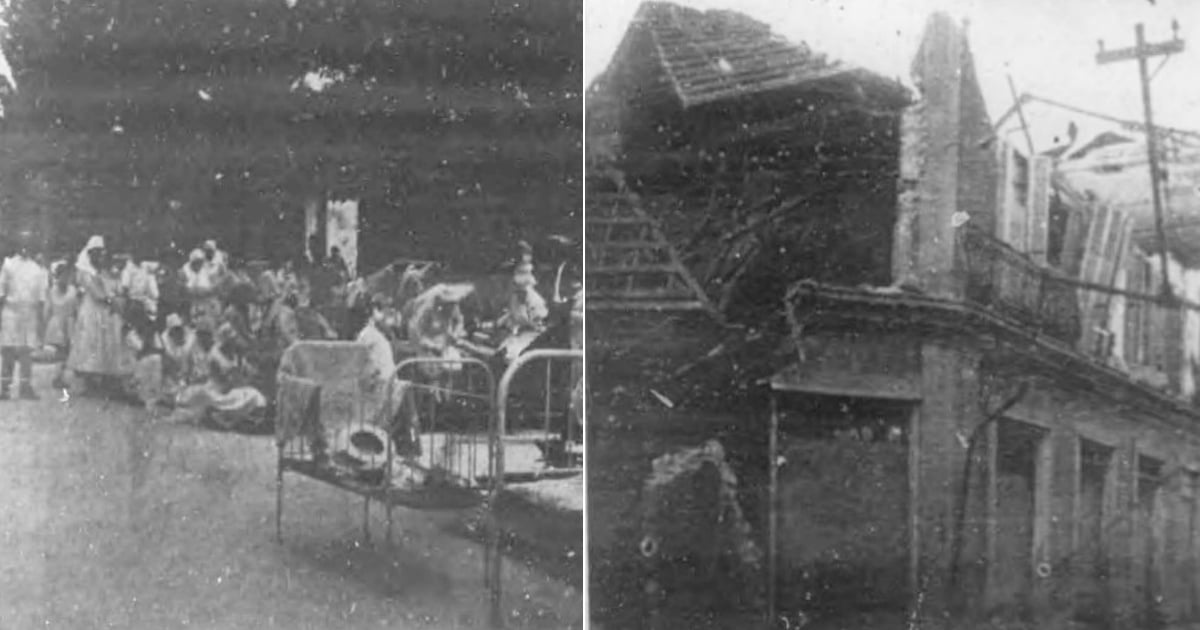
In recent history, on February 3, 1932, a magnitude 6.7 earthquake shook Santiago de Cuba for 18 seconds, leading to partial or total destruction of 60% of masonry buildings.
This event resulted in 13 fatalities and approximately 2,000 injuries, although other sources report lower figures.
A Bohemia magazine from that time left behind striking images and even listed the buildings that were damaged.
On May 25, 1992, a significant earthquake of magnitude 6.9 occurred in Cabo Cruz, regarded as one of the strongest recorded in the 20th century.
More recently, on January 28, 2020, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake struck the same region, marking it as the most intense in the modern history of the island.
Recent Events and Points of Interest
In 2023, the National Center for Seismological Research (CENAIS) reported a total of 7,475 earthquakes in the country, of which only 14 were felt by the population. The magnitudes of these events ranged from less than 3 to 5.9 degrees, with 70% of them concentrated along the Oriente fault.
This year, the most notable seismic activity occurred last Sunday in the municipality of Bartolomé Masó, in Granma, where two consecutive earthquakes were recorded with magnitudes of 6.0 and another of 6.7.
Despite being considered minor due to their short duration (the 6.7 quake lasted only seven seconds), they caused material damage and more than a dozen injuries.
What is an earthquake? Differences between terms
The language used to describe tectonic movements often creates confusion.
Many people believe that "sismo," "temblor," and "terremoto" have different meanings, but in reality, they are synonyms that describe any movement of the Earth's crust.
Popularly, a tremor (slight shaking) is distinguished from an earthquake (strong shaking), but scientists classify these events according to their magnitude (energy released) and intensity (effects perceived on the surface).
The magnitude of an earthquake is measured using different scales. For a long time, the Richter scale was the most commonly used, although today seismologists prefer to refer simply to "magnitude" and employ various more modern methodologies.
The recurrence of significant earthquakes in Cuba, especially in the eastern region, underscores the need for preventive measures and earthquake-resistant building codes, such as NC 46/2017. Furthermore, recent studies suggest a high likelihood that the Oriente fault will produce a magnitude 7 earthquake in the near future, highlighting the importance of preparedness and education to mitigate the impacts of these events.
The strongest earthquakes in Cuba have shown a recurrence period of over 100 years, which implies that high-magnitude events are not frequent but are highly destructive.
The list of the most significant earthquakes in the history of Cuba can be found at this link.
Filed under: