The United States has identified at least 12 Chinese facilities in Cuba that may be used by the Chinese regime to gather intelligence in the region.
The Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) in the United States indicated in a report that, based on satellite imagery and other intelligence sources, four of these facilities are essential for intercepting sensitive communications and monitoring strategic activities.
The identified sites are located in Bejucal (Mayabeque); in Wajay and Calabazar (Havana); and in El Salao (Santiago de Cuba).
According to the report, these facilities are equipped with advanced signals intelligence (SIGINT) technology and exhibit physical features that suggest espionage purposes, such as sophisticated antennas, perimeter fences, and military presence.
China and Cuba: An Evolving Alliance
For decades, the relationship between China and Cuba has been marked by increasing economic, political, and strategic cooperation.
However, recent research from the Center for Strategic and International Studies has shed new light on the extent of this partnership, indicating the possible existence of intelligence facilities in Cuba operated by China.
These revelations, based on analyses of satellite images and open sources, suggest that Beijing has significantly expanded its intelligence-gathering capabilities in the Caribbean, just a few kilometers from the United States.
For years, rumors about the presence of Chinese intelligence on the island had been sporadic and unconfirmed.
However, in June 2023, officials from the Biden administration acknowledged that China had access to espionage facilities in Cuba.
This recognition, followed by reports identifying as many as four potential sites, marks a turning point in the analysis of Cuba's strategic role in the context of global competition among major powers.
The strategic importance of Cuba.
Located less than 160 kilometers from the coast of Florida, Cuba offers a unique strategic position for signal intelligence (SIGINT) gathering.
The southern United States is home to significant military infrastructure, including command centers, space launch facilities, and naval bases.
For China, a SIGINT presence on the island represents an invaluable opportunity to monitor sensitive communications, military activities, and U.S. aerospace operations.
Additionally, control over strategic information in the Caribbean could provide Beijing with a significant advantage in a global competition scenario.
The facilities in Cuba also facilitate the interception of data from satellites and telecommunications networks, areas of particular interest to Chinese intelligence.
Identified Facilities
The CSIS research identified four locations in Cuba with characteristics suggesting their use for SIGINT collection:
It seems that there is no additional text provided after "BEJUCAL." Could you please provide the complete text you would like translated?
This historic complex, known for its role in the Missile Crisis of 1962, remains a key intelligence hub. Satellite imagery reveals an active and modernized infrastructure, including satellite dishes oriented toward geostationary satellites.
Its proximity to the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Space Force Station enables China to monitor space launches and gather critical data on advanced American technologies.
The text "EL SALAO" can be translated as "THE SALT," but it may also carry specific cultural or contextual meanings depending on its use. If you provide additional context, I can offer a more tailored translation.
Near Santiago de Cuba, this new facility has been under construction since 2021. Equipped with advanced high-frequency direction finding (HFDF) systems, it has the capability to track radio signals over distances of thousands of kilometers.
The connection of this project with Chinese investments in local infrastructure, such as the Moncada Cement Plant, reinforces the likelihood that it is geared toward strategic objectives.
It seems the text you provided is incomplete. Could you please provide the full text you would like me to translate?
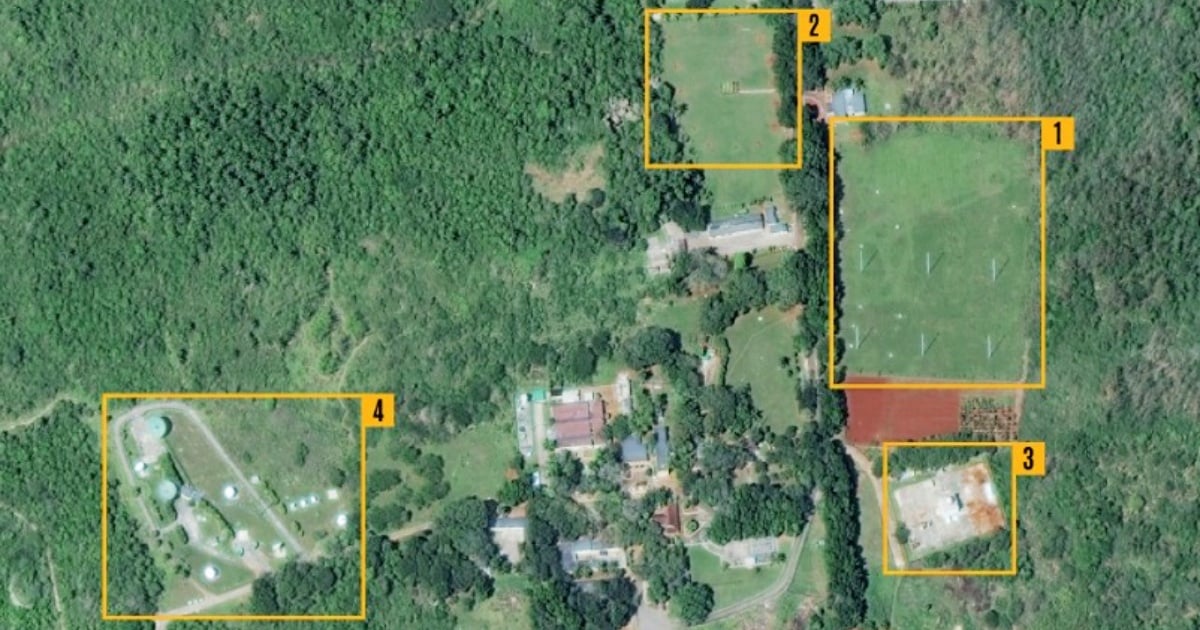
Less than 10 kilometers from Bejucal, this smaller facility has shown signs of steady expansion over the past 20 years.
Currently, the site houses 12 antennas of various sizes, as well as operation facilities and a small solar park that ensures power in case of failures in the Cuban electrical system.
With a dozen antennas, a solar park, and security measures in place, it appears to be designed for intercepting terrestrial signals and carrying out diversified SIGINT missions.
While the CSIS acknowledges that there are no satellite dishes at this location, suggesting a focus on intercepting terrestrial signals, it cites documents that indicate possible Chinese involvement in its construction or modernization.
CALABAZAR:
Although less documented, this facility is equipped with modern equipment for tracking satellites and gathering space intelligence.
In Calabazar, the report highlights recent improvements, such as the construction of a large solar park that began in 2012, as well as the presence of satellite and vertical antennas facing south.
Although there are no public records linking this base to China, Cuban defectors cited by the CSIS consider it part of the intelligence efforts on the island.
According to the study, the equipment in Calabazar could be used to monitor satellites in geostationary orbit, providing China with advanced capabilities to track both its space assets and the activities of other nations, including the United States.
The Role of SIGINT in China's Strategy
Signal intelligence is a cornerstone of modern espionage capabilities. It allows for the interception of communications and the tracking of military movements, providing a critical advantage in analyzing adversaries and competitors.
Despite advancements in data encryption, monitoring radio frequency and satellite signals remains valuable for gathering tactical and strategic information.
For China, expanding its SIGINT capabilities beyond its borders, particularly in a location so close to the United States, reinforces its ambition to become a dominant global player.
The data collected from Cuba could enhance the technological capabilities of the People's Liberation Army (PLA), providing Beijing with a unique insight into Washington's military and security activities in the Western Hemisphere.
Economic Crisis in Cuba: An Opportunity for Beijing
The growing influence of China in Cuba is closely linked to the economic crisis the island is experiencing.
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the Cuban economy has experienced a severe contraction, characterized by rampant inflation, fuel shortages, and a massive exodus of citizens.
In this context, China’s financial and technological assistance has been crucial for the government of Havana.
Beijing has financed infrastructure projects, including the port of Santiago de Cuba and solar parks, as well as providing telecommunications technology through companies such as Huawei and ZTE.
These initiatives not only strengthen bilateral ties but also position China as an indispensable partner for Cuba amid its economic isolation.
China's presence in Cuba poses significant challenges to regional security and strategic stability. The United States now faces a situation where a global adversary has access to intelligence facilities less than 160 kilometers from its borders.
This scenario highlights Cuba's significance during the Cold War, when it became a crucial focal point in the rivalry between Washington and Moscow.
Furthermore, the strengthening of cooperation between China and Cuba could extend beyond SIGINT, encompassing human intelligence (HUMINT) and other forms of espionage.
The history of Cuban intelligence, with a sophisticated network focused on the United States, suggests that Havana could share critical information with Beijing, further enhancing China's capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions about Chinese Espionage Bases in Cuba
How many Chinese espionage bases have been identified in Cuba?
At least 12 Chinese facilities in Cuba have been identified as potentially being used to collect intelligence information in the region, according to a report by the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) in the United States.
Where are the Chinese espionage bases located in Cuba?
The identified bases are located in Bejucal (Mayabeque); in Wajay and Calabazar (Havana); and in El Salao (Santiago de Cuba). These facilities are equipped with advanced signals intelligence (SIGINT) equipment and display physical characteristics that suggest espionage purposes.
Why is Cuba's location strategically important for Chinese espionage?
Cuba offers a unique strategic position for signals intelligence (SIGINT) gathering, being located less than 160 kilometers from the coast of Florida, close to vital U.S. military infrastructure. This provides China with significant intelligence insight into the United States.
What has been the Cuban government's response to the accusations of Chinese espionage?
The Cuban government has repeatedly denied the existence of Chinese espionage bases on the island, labeling the accusations as unfounded and part of a "campaign of intimidation." Cuban authorities have dismissed any agreements with China regarding the establishment of espionage bases on their territory.
Filed under: