Related videos:
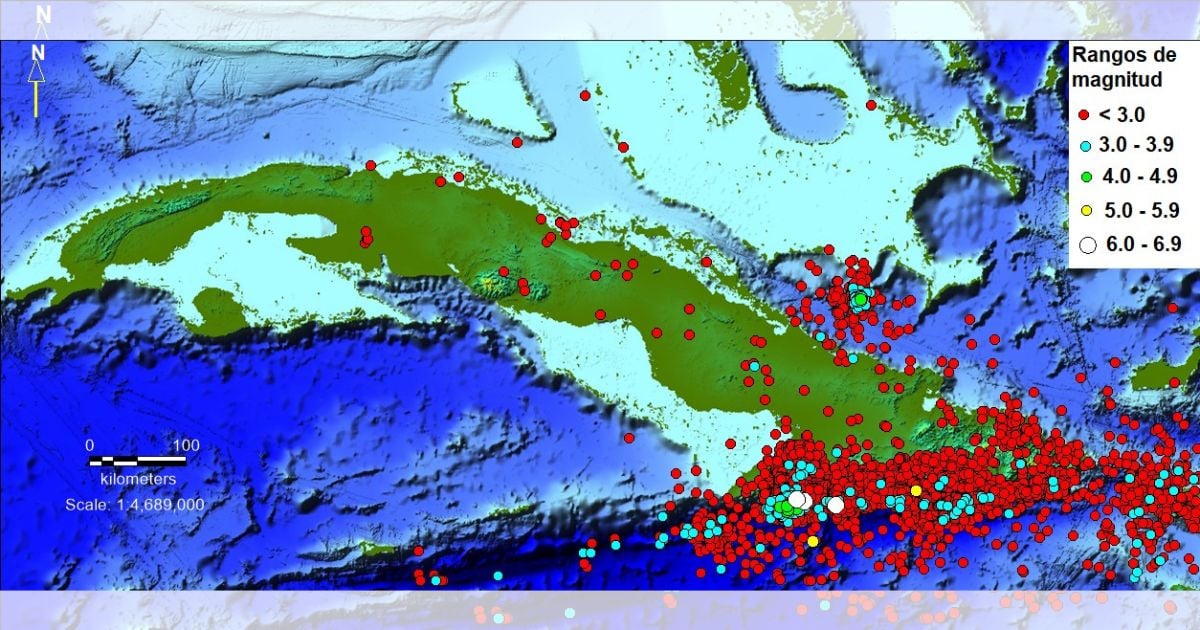
The year 2024 has been the most active in the seismic history of the island, with a total of 12,806 earthquakes recorded in the national territory.
This record was marked by the occurrence of three significant seismic events, two of which took place on November 10 with magnitudes of 6.0 and 6.7, and a third on December 23, with a magnitude of 6.1.
Enrique Arango Arias, head of the National Seismological Service of Cuba, which is part of the National Center for Seismological Research (CENAIS), reported via Facebook that these earthquakes originated in sections of the Oriente transform fault, an area characterized by predominant lateral sliding movements.
The first two occurred about 40 kilometers southeast of Pilón, in Granma province, while the third had its epicenter south of the municipality of Guamá, in Santiago de Cuba.
Since the onset of seismic activity on January 10, until the end of the year, there were 8,873 aftershocks associated with the earthquakes in November, and 446 aftershocks following the event on December 23.
According to Arango, it is normal for this type of aftershocks to continue in the months that follow, although they should gradually decrease in both quantity and intensity over time.
The report indicates that out of more than 12,800 recorded earthquakes, 20 were reported as perceptible. Of these, 10 occurred in the Santiago-Baconao area, 5 in inland locations such as Moa, Baracoa, Sibanicú, and Varadero, and 5 in the Pilón-Chivirico region, where the three most significant earthquakes of the year were recorded.
Additionally, it is estimated that 143 potentially perceptible earthquakes were not reported in bulletins, as many had lower magnitudes, even though they could be felt in localities near the epicenters.
One of the most significant earthquakes was the 6.7 magnitude quake on November 10, the impact of which was assessed by specialists from CENAIS.
According to the European Macroseismic Scale (EMS/1998), intensities reached up to VIII degrees in towns such as Pilón, Bartolomé Masó, Mota, and Marea del Portillo, while places like Yara, Cayo Espino, and Media Luna recorded intensities of VII degrees.
In places like Niquero, Campechuela, and Manzanillo, the intensity ranged from VI to VII degrees, while Cauto Cristo reported V degrees.
The most severe damage occurred in buildings without adequate reinforcements, many of which had already been affected by historic earthquakes such as those on February 19, 1976, and May 25, 1992, and had never been rehabilitated.
The lack of structural preparedness, combined with widespread panic among the population—where 100% of those surveyed reported feeling the seismic movements in November—highlighted the vulnerability of communities to such events.
2024 not only marks a record in terms of seismic activity, but it also highlights the urgent need to strengthen prevention measures, structural reinforcement, and community preparedness in the country’s most vulnerable areas.
The high seismic activity recorded emphasizes the importance of maintaining constant vigilance over the Eastern transform fault and other areas of high seismic activity in the national territory.
Frequently Asked Questions about Seismic Activity in Cuba in 2024
How many earthquakes were recorded in Cuba in 2024?
In 2024, Cuba recorded a total of 12,806 earthquakes. These events included three major tremors with magnitudes of 6.0, 6.7, and 6.1, making this year the most active in the island's seismic history.
What was the magnitude of the main earthquakes that occurred in Cuba in 2024?
The main earthquakes recorded in 2024 in Cuba had magnitudes of 6.0, 6.7, and 6.1. These occurred on November 10 and December 23, primarily affecting the provinces of Granma and Santiago de Cuba.
How has seismic activity affected the infrastructure in the eastern region of Cuba?
The intense seismic activity in 2024 caused significant damage to over 3,752 buildings in the eastern region of Cuba, particularly in Granma province. The earthquakes left many residents living in precarious conditions due to the lack of adequate structural reinforcements.
What measures has the Cuban government taken in response to the seismic crisis in the East?
The Cuban government has set up temporary shelters to house affected families, but this measure has been criticized for its limited scope and for neglecting other equally impacted communities. The situation underscores the urgent need to strengthen infrastructure and preventive measures on the island.
Filed under: